What Are Complex Carbohydrates? + 28 Healthy Options to Include in Your Diet

Carbohydrates, or carbs, are one of the body’s primary macronutrients—nutrients needed in large amounts to function properly. They're found in foods like fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes. Your body relies on carbs for energy, digestive support, and maintaining balanced blood sugar levels.
You've likely heard that some carbs are better than others. In general, complex carbohydrates are healthier than simple or refined ones.
But what makes complex carbs different—and why should you eat more of them?
Simple vs. Complex Carbohydrates
All carbs are made of sugar molecules such as glucose, fructose, and galactose, and are categorized based on the number of sugar units they contain.
Two Main Types of Carbs
-
Simple carbohydrates – One or two sugar molecules; quickly digested and absorbed.
-
Complex carbohydrates – Three or more sugar molecules; digested more slowly, providing longer-lasting energy.
Simple Carbs
Monosaccharides (single sugar units):
-
Glucose
-
Fructose
-
Galactose
Disaccharides (two sugar units):
-
Sucrose (glucose + fructose)
-
Lactose (glucose + galactose)
-
Maltose (glucose + glucose)
These sugars are naturally found in fruit and dairy, but also in many processed foods like soda, candy, and baked goods. They spike blood sugar quickly and provide little nutritional value when consumed in excess.
Complex Carbs
Complex carbohydrates, also known as polysaccharides, consist of longer chains of sugar molecules. They take more time to digest and result in slower, more steady blood sugar increases.
Types of complex carbs:
-
Starch – Found in foods like grains and legumes.
-
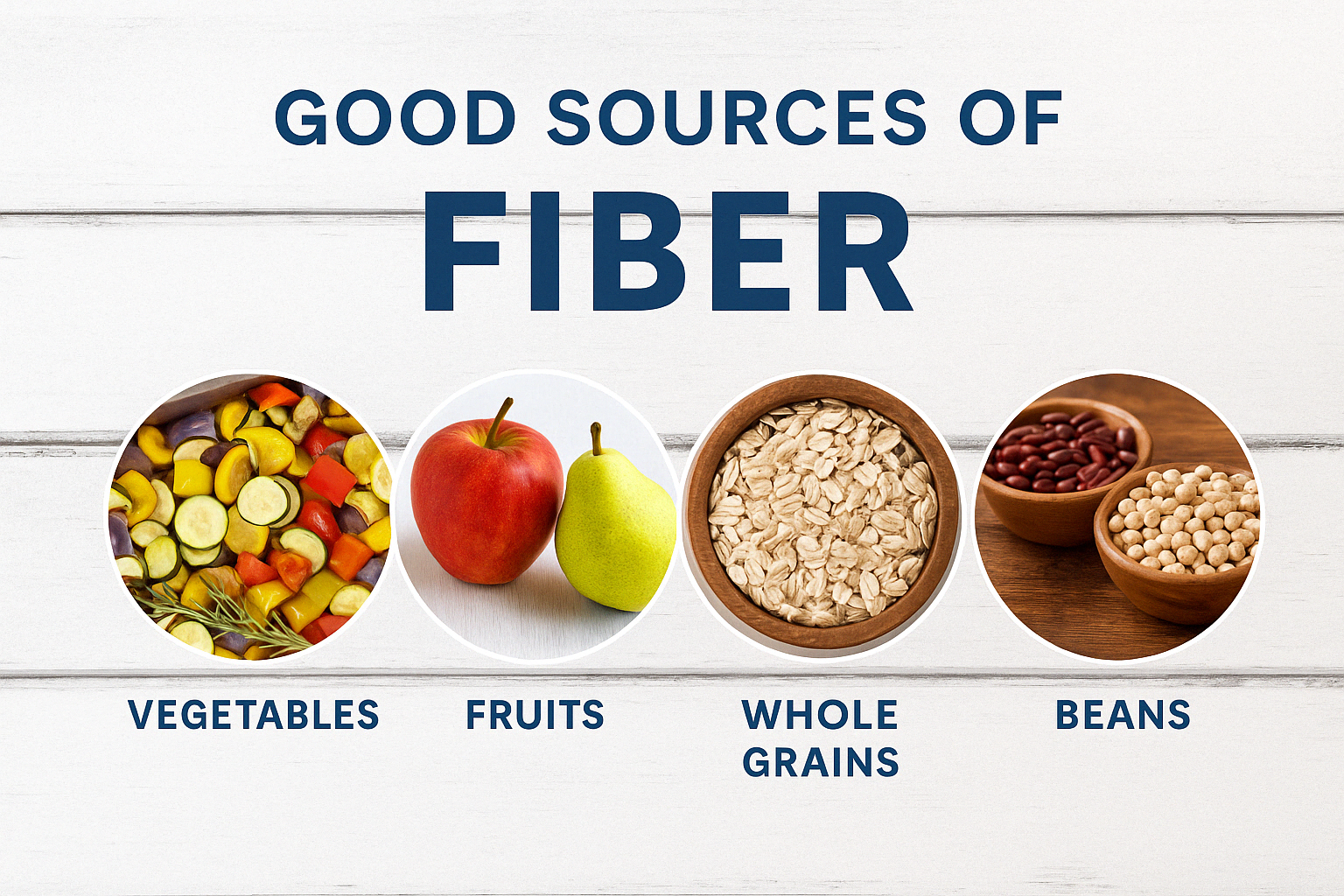
Fiber – Found in plant foods; supports gut health and digestion.
-
Glycogen – Stored in the muscles and liver; used as energy.
Fiber-rich carbs are associated with lower risks of chronic diseases and help with fullness and weight control.
28 Complex Carbohydrate Foods to Add to Your Diet
Incorporating more complex carbs into your diet is an excellent way to boost nutrition and support your health. Here are 28 healthy options:
1. Whole Grains
Whole grains retain all three parts of the grain: bran, germ, and endosperm—offering fiber and essential nutrients.
-
Oats
-
Brown rice
-
Quinoa
-
Millet
-
Buckwheat
-
Farro
-
Barley
2. Legumes (Pulses)
Packed with fiber, protein, and key vitamins and minerals, legumes are a powerhouse of nutrition.
-
Lentils
-
Chickpeas
-
Black beans
-
Kidney beans
-
Pinto beans
-
Cannellini beans
-
Green peas
3. Starchy Vegetables
These vegetables are rich in complex carbs and loaded with vitamins:
-
Sweet potatoes
-
Regular potatoes
-
Beets
-
Butternut squash
-
Acorn squash
-
Delicata squash
-
Parsnips
4. Fruits
Many fruits are a natural source of complex carbs, along with fiber and antioxidants.
-
Apples
-
Bananas
-
Blueberries
-
Strawberries
-
Oranges
-
Mangoes
-
Peaches
Simple Carbs to Cut Back On
While naturally occurring sugars in fruit are okay, added sugars and refined carbs should be limited.
Refined Grains
These grains have been stripped of fiber and nutrients:
-
White bread
-
White rice
-
Crackers made from refined flour
Added Sugars
Common sources include:
-
Table sugar
-
High-fructose corn syrup
-
Honey (when overused)
The American Heart Association recommends a maximum of 38g/day for men and 25g/day for women.
Sugary Foods and Drinks
Many processed foods are loaded with hidden sugars:
-
Soda
-
Candy
-
Ice cream
-
Sweetened yogurt
-
Granola
-
Sauces and dressings
-
Sweetened coffee drinks
Replacing these with whole foods and water can improve your health significantly.
In Summary
Complex carbs digest slowly, help regulate blood sugar, and are rich in essential nutrients. Focusing on whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables—while cutting down on sugar and refined products—can enhance your diet and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.























.webp)
.webp)
.webp)









